Connecticut heating solutions decoded: from game-changing heat pumps to efficient boilers and furnaces!
Heating Systems, Compared
At Home Comfort Practice, we're passionate about giving you the best insights into heating solutions tailored for Connecticut's unique climate. Dive into our comparison of heating systems. Discover why heat pumps might just be the game-changer you've been searching for. Learn about all the incentives available for heat pumps, energy efficient boilers, furnaces and more. Let's heat things up and get started!
Heat pumps: How they work, configurations & types. Heat Pump Basics
Heat pumps operate on a simple principle: instead of generating heat, they transfer it. Using a refrigeration cycle, they can extract heat from the outside air or ground and move it indoors during colder months, and reverse the process during warmer months to cool your home. This method of transferring heat, rather than producing it through combustion or electric resistance, makes heat pumps incredibly efficient. In fact, a well-installed heat pump can deliver up to three times more heat energy to a home than the electrical energy it consumes. For Connecticut residents, this means a system that adapts to both the chilly winters and humid summers, providing year-round comfort with reduced energy consumption.
There are several types of heat pumps, each with its own advantages:
-
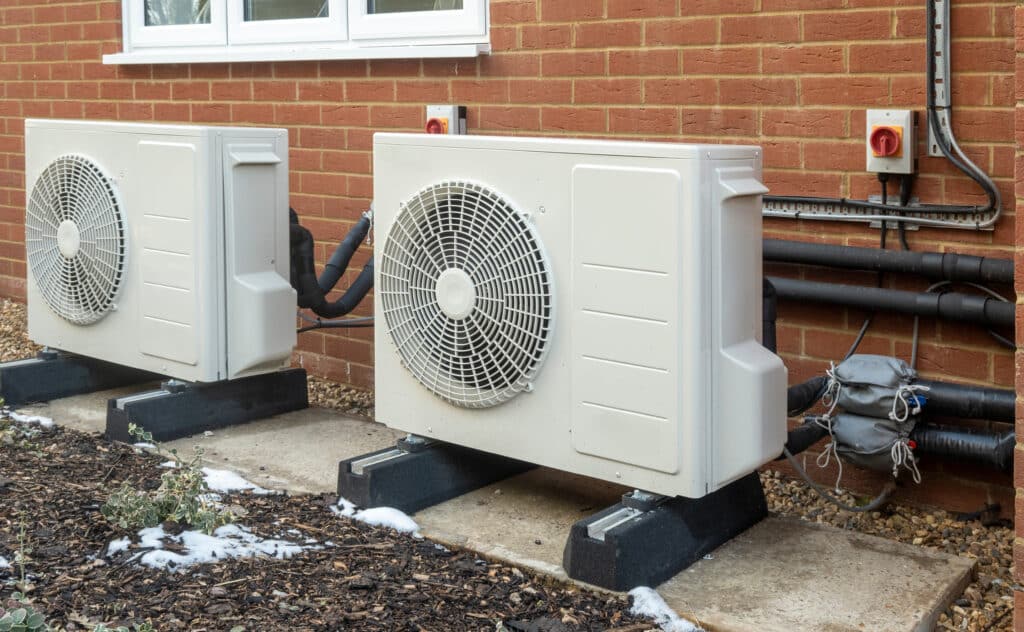
Air-Source Heat Pumps: These are the most common and extract heat from the outside air. Advanced models can even function efficiently in colder climates, making them suitable for Connecticut's winters.
-
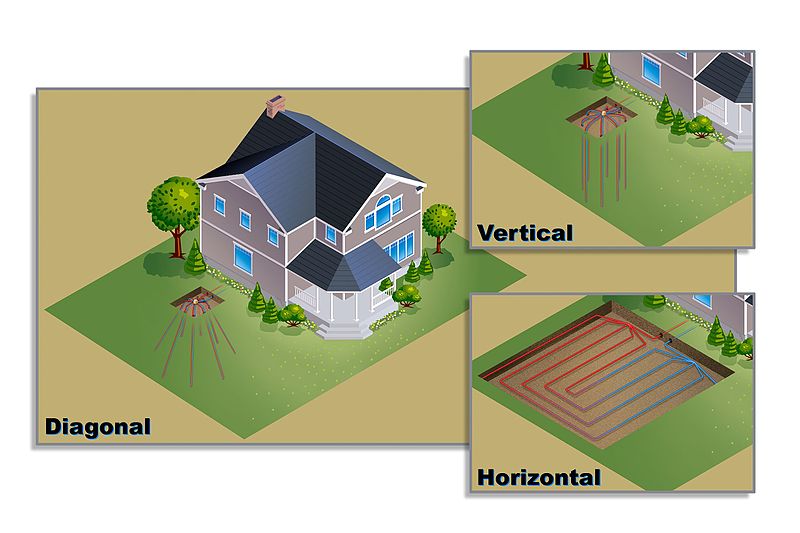
Ground-Source or Geothermal Heat Pumps: These systems harness the stable temperatures of the earth by extracting heat from the ground or underground water sources. Given Connecticut's fluctuating temperatures, ground-source heat pumps offer consistent performance year-round, making them an ideal choice for the state.
-
Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pumps: Perfect for homes without ductwork, these systems allow for zoning, letting you heat or cool specific areas of your home. They're flexible and can be a great fit for older Connecticut homes or specific room additions.
The best fit depends on individual household needs, existing infrastructure, and budget considerations. For Connecticut's varied climate, ground-source heat pumps produce consistent efficiency throughout the year. However, the costs and lead times can be daunting. Air source heat pumps are less costly, much easier to install and offer many similar advantages. Our experts will guide you towards the optimal system based on your unique needs.
Heat pumps: How do they mearue up to alternatives? Heat Pumps vs The Rest
We'll pit the traditional stalwarts - Gas/Oil Furnaces and Boilers, against the modern marvel that is the Heat Pump. How do they stack up in efficiency & cost? What incentives are available? Let's take a look!
Gas and oil furnaces rely on combustion, burning fuel to produce heat. This process inherently has energy losses and emits greenhouse gases. On the other hand, heat pumps, whether air-source or ground-source, work by transferring heat. They can extract heat from the outside air or the stable temperatures of the earth and move it indoors. In Connecticut, with its varied climate, heat pumps can operate at efficiencies of up to 400%, meaning for every unit of energy they consume, they can provide up to four units of heat energy. In Connecticut, with its cold winters and warm summers, heat pumps offer a dual advantage: they can both heat and cool a home using the same system. Additionally, because heat pumps don't rely on combustion, they eliminate the risk of carbon monoxide exposure and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This makes them a more environmentally friendly option compared to traditional furnaces.This efficiency, combined with the ability to both heat and cool homes, makes heat pumps a versatile and eco-friendly solution for Connecticut residents.
Gas and oil boilers generate heat by burning fuel to warm water, which is then circulated through radiators or under-floor heating systems. This method, while effective, can sometimes be less energy-efficient than heat pump systems. Heat pumps, leveraging the principles of vapor-compression refrigeration, extract and transfer heat from the environment, either from the air or the ground. This process can be more energy-conservative, especially when considering the full fuel-to-heat chain of boilers. For Connecticut residents, the versatility of heat pumps is a significant advantage. They can efficiently heat homes during the chilly winters and cool them during the humid summers. Furthermore, the absence of combustion in heat pumps means no on-site emissions or potential gas leaks, enhancing safety and environmental sustainability.
Electric resistance heating operates by passing electricity through resistive elements, converting electrical energy directly into heat. While this process is straightforward, it's not always the most energy-efficient, especially when compared to heat pumps. Heat pumps utilize a refrigeration cycle, transferring heat from one place to another, rather than generating it directly. This method can be up to three times more efficient than resistance heating. In Connecticut, where energy costs and environmental concerns are paramount, heat pumps can offer significant savings on electricity bills. Moreover, the dual-functionality of heat pumps, providing both heating in winter and cooling in summer, makes them a comprehensive solution for Connecticut's varied seasonal demands.
Heat & Cool with one system? But at what price? Heat Pump Costs & Rebates
Connecticut's Energize CT program provides substantial rebates for heat pumps:
-
For Air Source Heat Pumps, there's a rebate of $1,250 per ton. These systems generally cost between $5,000 to $25,000. Residents can claim up to a maximum rebate of $15,000, depending on the equipment size. Over its lifetime, an average savings of $15,000 can be expected.
-
For Ground Source Heat Pumps, the rebate is also $1,250 per ton. The initial cost for these systems ranges from $17,000 to $34,000. Like the air source variant, the maximum rebate available is $15,000. Impressively, homeowners can anticipate lifetime savings of around $50,000.
| Energize CT Rebate: $1250 per Ton | |
|---|---|
| Avg. Initial Cost | $5000-$25000 |
| Max Rebate | $15000 |
| Avg. Lifetime Savings | $15000 |
Claim up to $15,000 combined incentives for qualifying air source heat pumps. Energize CT heat pump rebates are based on equipment size (tonnage).
| Energize CT Rebate: $1250 per Ton | |
|---|---|
| Avg. Initial Cost | $17000-$34000 |
| Max Rebate | $15000 |
| Avg. Lifetime Savings | $50000 |
Claim up to $15,000 in Energize CT ground source heat pump rebates for qualifying equipment.
Under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), significant rebates are available for heat pump air conditioner/heater systems: The IRA Electrification Rebate offers up to $8,000 for these systems.
| IRA Electrification Rebate: $8000 | |
|---|---|
| Upfront Discount | 50%-100% of Costs |
| Avg. Initial Cost | $8000-$35000 |
Claim up to $8,000 in Inflation Reduction Act rebates for heat pump air conditioner/heater systems. Low-income households with incomes that are below 80 percent of the Area Median Income (AMI) are eligible to receive 100 percent coverage of their heat pump costs up to $8,000. Moderate-income households with incomes between 80 percent and 150 percent of the AMI are eligible to receive 50 percent coverage of their heat pump costs up to $8,000.
-
Heat Pump Air Conditioner/Heater: The 25C tax credit offers homeowners 30% of costs, capped at $2,000 annually. It offsets taxes owed, requires sufficient tax liability, and can be combined with other rebates. Renters may not qualify.
-
Ground Source Heat Pumps: The 25D tax credit provides a 30% credit for installing these pumps, with no cap on the amount.
| IRA Tax Credit: 30% of Costs | |
|---|---|
| 25C Max Credit | $2000 |
| 25D Max Credit | Uncapped |
The 25C tax credit from the Inflation Reduction Act offers homeowners a 30% non-refundable credit, capped at $2,000 per year, for installing a Heat Pump Air Conditioner/Heater. It can offset taxes owed, but not provide a refund. It requires sufficient tax liability, can be combined with other funding programs, and may reduce installation costs when combined with other rebates. Renters may not be eligible.
| IRA Tax Credit: .30% of Costs | |
|---|---|
| 25C Max Credit | Uncapped |
| 25D Max Credit | Uncapped |
The Inflation Reduction Act’s Section 25D tax credit provides homeowners with a 30% tax credit for installing a geothermal or ground-source heat pump.
Boilers Vs Heat Pumps
It's a face-off between traditional Boilers and the state-of-the-art Heat Pump. Who takes the crown for efficiency and cost-effectiveness? And what rebates are on offer? Let's explore!
Boilers heat water and distribute the hot water or steam through pipes to radiators or under-floor heating systems. Heat pumps, in contrast, use a refrigeration cycle to transfer heat between the home and the outside environment, distributing it via air handlers or ductwork.
Boilers are typically rated using AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency), which measures how efficiently they convert fuel into heat. Modern high-efficiency boilers can achieve AFUE ratings of up to 90% or more, meaning they convert 90% of the fuel they burn into usable heat. On the other hand, heat pumps are rated using HSPF (for heating) and SEER (for cooling). A high-efficiency heat pump can have an HSPF rating of 8 to 10, indicating that it can be 200-300% efficient in transferring heat. This means that for every unit of electricity they consume, they can provide 2 to 3 units of heating or cooling. In terms of energy efficiency, heat pumps often have an edge, especially in milder climates.
Boiler Rebates
Yes, Connecticut offers rebates for certain boiler systems and their components. If you're considering a Natural Gas Boiler, the Energize CT program provides a rebate of $750 per unit. The average initial cost for these boilers ranges between $4,000 to $20,000, and with the rebate, you can reduce your upfront investment by up to $750. Over the boiler's lifetime, you can expect average savings of around $20,000.
Additionally, if you're looking to purchase a Boiler Circulator Pump, there's a rebate of $35 per unit available. These pumps typically cost between $150 to $300, and the rebate can help offset this initial cost. Over the pump's lifespan, homeowners can anticipate average savings of approximately $4,800.
| Energize CT Rebate: $750 per Unit | |
|---|---|
| Avg. Initial Cost | $4000-$20000 |
| Max Rebate | $750 |
| Avg. Lifetime Savings | $20000 |
Claim a $750 rebate for qualifying Natural Gas Boilers
| Energize CT Rebate: $35 per Unit | |
|---|---|
| Avg. Initial Cost | $150-$300 |
| Max Rebate | $35 |
| Avg. Lifetime Savings | $4800 |
Claim a $35 rebate for a new Boiler Circulator Pump
Furnaces Vs Heat Pumps
Pitting age-old Natural Gas furnaces against the contemporary Heat Pump. Who wins in the battle of efficiency and cost? And what about rebates? Join us for the breakdown!
Furnaces generate heat by burning fuel, typically natural gas. The combustion process heats air, which is then circulated through the home via ducts. Heat pumps, on the other hand, operate on a refrigeration cycle. Instead of producing heat, they transfer it from one place to another, extracting warmth from the outside air or ground and moving it indoors during the winter.
Natural gas heating systems are often measured in terms of AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency), which indicates the percentage of consumed fuel that's converted into usable heat. High-efficiency natural gas heating systems can achieve AFUE ratings close to 90%, indicating that they convert 90% of the gas they burn into usable heat. Heat pumps, on the other hand, are rated using COP (Coefficient of Performance) for their heating mode. A typical heat pump can have a COP ranging from 2 to 4, meaning it can deliver 2 to 4 times more energy than it consumes. This high efficiency is due to the heat pump's mechanism of transferring heat rather than generating it. In terms of energy use, heat pumps can be more efficient than natural gas heating systems, especially in moderate climates.
The combustion process in furnaces, especially those that burn natural gas, produces byproducts like carbon dioxide. Heat pumps, being electric and not relying on combustion, have no direct emissions. In Connecticut, where there's a push for cleaner energy solutions, heat pumps align with environmental goals, reducing the household's carbon footprint.
While furnaces, especially older models, might have a lower upfront cost, heat pumps can lead to lower monthly energy bills due to their high efficiency. Moreover, when natural gas prices are low, it might make these systems appear cost-effective in the short term. The long-term perspective needs to consider factors like price volatility and potential increases in natural gas costs. Heat pumps, with their ability to transfer heat rather than generate it, can offer consistent energy efficiency, translating to potential savings on monthly energy bills. Furthermore, Connecticut offers energy rebates for efficient systems like heat pumps, which can significantly offset the initial investment. When considering these rebates, the potential for lower monthly bills, and the environmental benefits, heat pumps emerge as a forward-thinking, efficient choice for many Connecticut residents.
Furnace Rebates
In Connecticut, the Energize CT program offers rebates for specific furnace systems. For those considering a Natural Gas Furnace, there's a rebate of $650 per unit. These furnaces typically have an initial cost between $1,800 to $2,300. With the rebate, residents can reduce this upfront cost by up to $650. Over the furnace's lifetime, you can expect to save an average of $1,550. This rebate initiative makes it more economical for Connecticut residents to invest in energy-efficient furnaces.
| Energize CT Rebate: $650 per Unit | |
|---|---|
| Avg. Initial Cost | $1800-$2300 |
| Max Rebate | $650 |
| Avg. Lifetime Savings | $1550 |
Claim a $650 rebate for qualifying Natural Gas Furnaces.
Qualify for Air Conditioning Rebates by Getting a Home Energy Audit Get Qualified for AC Rebates
$0
$0
Weatherization Service Value$0
Average Annual Energy Savings$0
Average 1st Year SavingsInstall. Repair. Replace. Maintain. HCP Offers a Full Range of HVAC Services. More HVAC Services
Heating
Learn More...
Air Conditioning
Learn More...
HVAC Rebates
Learn More...
Ductwork
Learn More...
Indoor Air Quality
Learn More...